Advanced Coatings for Superior Corrosion and Wear Resistance
Corrosion and wear pose significant challenges across various industries, leading to substantial economic losses and structural failures. Recent advancements in coating technologies offer promising solutions to enhance the durability and longevity of materials exposed to harsh environments.
This article explores the development of advanced coatings for corrosion and wear resistance, highlighting the innovative materials and techniques that have emerged in this field. Key developments include the use of metallic, inorganic, polymeric, and nanomaterial-based coatings, each providing unique properties that enhance protection. The integration of smart coatings with self-healing capabilities further exemplifies the progress in this area, offering long-term and reliable protection against corrosion and wear. Explore Nanografi's advanced materials to enhance your strategies for corrosion and wear resistance, providing reliable and long-lasting protection.
Introduction
Corrosion is the chemical or electrochemical degradation of materials, primarily metals, due to environmental interactions. Wear is the mechanical degradation resulting from friction, abrasion, or impact. Both phenomena significantly impact various industries, leading to high economic costs, structural integrity issues, and increased maintenance requirements.
Why Advanced Coatings are Important?
Advanced coatings serve as a critical line of defense against corrosion and wear. By forming protective barriers, these coatings prevent direct exposure of the underlying materials to damaging elements, thereby prolonging their service life and performance.
✓ Protection and Durability
Advanced coatings significantly improve the lifespan of materials by providing robust protection against environmental factors such as corrosion, wear, and UV radiation. For instance, anti-corrosive coatings are widely used in the marine and automotive industries to prevent rust and degradation, thereby extending the service life of metal components.
✓ Enhanced Performance
These coatings are designed to impart specific properties that enhance the performance of the substrate. For example, thermal barrier coatings in aerospace applications protect engine components from extreme temperatures, ensuring operational efficiency and safety. Similarly, hydrophobic coatings on medical devices prevent contamination and improve hygiene.
✓ Energy Efficiency
Energy-efficient coatings, such as low-emissivity (Low-E) coatings on windows, reduce energy consumption by reflecting infrared radiation while allowing visible light to pass through. This helps in maintaining indoor temperature, reducing the need for artificial heating and cooling, and consequently lowering energy costs.
✓ Aesthetic Appeal
In the consumer goods and automotive industries, advanced coatings provide an aesthetically pleasing finish while offering additional protection. High-gloss, scratch-resistant coatings on electronic devices and vehicles enhance their visual appeal and market value.
✓ Functional Integration
Advanced coatings can integrate multifunctional properties, combining protection with other functionalities such as anti-microbial, anti-fouling, and self-cleaning capabilities. For instance, anti-microbial coatings in healthcare settings reduce the spread of infections, contributing to improved patient safety.
✓ Environmental Benefits
Eco-friendly advanced coatings, such as waterborne and powder coatings, have lower volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions compared to traditional coatings. This contributes to a reduction in air pollution and a smaller environmental footprint, aligning with sustainability goals.
✓ Innovation in Material Science
The development of advanced coatings is a testament to the advancements in material science and nanotechnology. For example, nanocoatings with nanoparticle additives provide unprecedented properties such as superhydrophobicity and enhanced mechanical strength, opening new possibilities for innovative applications.
✓ Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial cost of advanced coatings may be higher, their long-term benefits include reduced maintenance and replacement costs. By enhancing durability and performance, these coatings contribute to significant cost savings over the lifecycle of the coated product.
Graphene-based materials significantly enhance the corrosion resistance of coatings by providing a highly effective barrier against moisture and oxygen. Learn more.
Types of Advanced Coatings
Advanced coatings encompass a wide range of technologies designed to enhance the performance, durability, and aesthetic properties of various materials. These can be broadly grouped into the following categories based on their primary functions and applications:
Anti-Corrosion Coatings
Anti-corrosion coatings are designed to protect metal surfaces from oxidation and corrosion, which can significantly extend the lifespan of metal structures and components. This category includes:
Metallic Coatings
Metallic coatings, including novel zinc alloys and metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), offer robust protection against corrosion. These coatings function by forming sacrificial layers that preferentially corrode, thereby protecting the underlying metal. For instance, ZnAl diffusion layers on carbon steel have shown significant improvements in corrosion resistance through a mechanical energy-aided diffusion method.
Inorganic Coatings
Inorganic coatings, such as passivating oxide layers, provide a thin yet effective barrier against corrosion. Techniques like plasma-electrolytic oxidation (PEO) and micro arc oxidation (MAO) produce ceramic oxide layers on light metals, enhancing their resistance in marine environments and other corrosive conditions. Additionally, boride cermet coatings and carbide-based coatings contribute to both wear and corrosion resistance.
Polymeric Coatings
Polymeric coatings are widely utilized for their excellent adhesion, electrical insulation, and mechanical properties. Innovations in polymeric coatings involve the incorporation of micro/nano fillers and corrosion inhibitors to enhance their protective qualities. Superhydrophobic coatings and hybrid polymeric systems have demonstrated improved erosion and corrosion resistance, particularly in challenging environments.
Nanomaterial-Based Coatings
Nanomaterials have brought about a significant transformation in the field of advanced coatings, offering unparalleled properties that enhance the protective capabilities of coatings. These materials exhibit unique characteristics such as high specific surface area, excellent mechanical strength, and superior barrier properties, which make them ideal for integration into coating systems. Here, we delve deeper into some of the key nanomaterials used in advanced coatings:
- Graphene Oxide (GO)
Graphene oxide (GO) is a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a two-dimensional honeycomb lattice, functionalized with oxygen-containing groups. GO's exceptional mechanical properties, high thermal stability, and excellent barrier properties make it a popular choice for advanced coatings. GO can form a dense, impermeable layer that significantly reduces the permeability of corrosive agents, thereby enhancing the corrosion resistance of the underlying substrate.
Applications:
- Corrosion Protection: GO coatings are used to protect metal surfaces from corrosion by forming a physical barrier that impedes the ingress of moisture and corrosive ions.
- Mechanical Reinforcement: When incorporated into polymer matrices, GO enhances the mechanical strength and durability of the coatings.
- Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs)
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are cylindrical nanostructures composed of graphene sheets rolled into a tube. They exhibit extraordinary electrical conductivity, mechanical strength, and chemical stability, making them suitable for a variety of coating applications.
Applications:
- Conductive Coatings: CNTs are used to create conductive coatings for electronic devices, providing both protection and electrical conductivity.
- Reinforcement: CNTs enhance the mechanical properties of coatings, including toughness, tensile strength, and wear resistance.
- Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2)
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) is a layered material with excellent lubricating properties and high thermal stability. MoS2 is widely used in coatings to reduce friction and wear, making it an essential component in lubricating and protective coatings.
Applications:
- Lubricating Coatings: MoS2 is used in industrial applications where reducing friction is crucial, such as in machinery and automotive parts.
- Corrosion Resistance: MoS2 enhances the corrosion resistance of coatings by providing a physical barrier and reducing wear.
Smart Coatings and Self-Healing Technologies
Smart coatings and self-healing technologies represent a significant advancement in the field of anti-corrosion coatings. These coatings are designed to autonomously repair damage and restore their protective functions, ensuring sustained protection against corrosion.
Self-Healing Mechanisms
Self-healing coatings are designed to autonomously repair damage and restore their protective functions. These coatings employ intrinsic or extrinsic mechanisms to achieve self-repair. Intrinsic self-healing relies on the reorganization of molecular chains within the material, while extrinsic self-healing involves the release of active agents, such as corrosion inhibitors, from micro/nano carriers embedded in the coating.
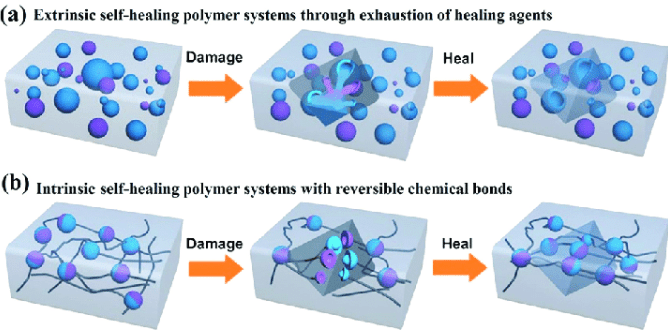
Figure 1. A schematic representation of self-healing polymer systems, showcasing (a) an extrinsic self-healing mode and (b) an intrinsic self-healing mode.
Micro/Nano Carriers
Micro/nano carriers play a pivotal role in smart coatings by storing and releasing corrosion inhibitors upon the onset of corrosion. These carriers are designed to be compatible with the coating matrix, have high loading capacities, and remain stable in various environmental conditions. Examples include mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSN), cerium oxide (CeO2) carriers, and metal-organic frameworks (MOFs).
Stimuli-Responsive Behavior
Smart coatings can release corrosion inhibitors in response to specific stimuli, such as changes in pH, temperature, or mechanical damage. This targeted release mechanism ensures that inhibitors are deployed only when needed, maximizing their efficacy and prolonging the protective performance of the coating.
Conclusion
The development of advanced coatings for corrosion and wear resistance has made significant strides, incorporating a diverse range of materials and technologies to address the multifaceted challenges posed by harsh environments. Metallic, inorganic, polymeric, and nanomaterial-based coatings each offer unique advantages, enhancing the durability and performance of protected materials. The advent of smart coatings with self-healing capabilities further underscores the potential for long-term, reliable protection. As research continues, the integration of these innovative coatings into industrial applications promises to reduce economic losses, improve safety, and extend the lifespan of critical infrastructure and components.
To follow the latest developments and innovations related to nanotechnology, visit Blografi.
References
Anti-Corrosive Nanocoatings - Nanografi Nano Technology. (n.d.). Retrieved July 9, 2024, from https://nanografi.com/blog/anticorrosive-nanocoatings/
Anti-rust Nano Coating Paints in Automotive - Nanografi Nano Technology. (n.d.). Retrieved July 9, 2024, from https://nanografi.com/blog/antirust-nano-coating-paints-in-automotive-/
Baruwa, A.D., Akinlabi, E.T., Oladijo, O.P. (2020). Surface Coating Processes: From Conventional to the Advanced Methods; a Short Review. In: Emamian, S.S., Awang, M., Yusof, F. (eds) Advances in Manufacturing Engineering. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-5753-8_44
Hughes, A. E., Johnston, P., & Simons, T. J. (2022). Self-healing coatings. Recent Advances in Smart Self-Healing Polymers and Composites, Second Edition, 217–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-823472-3.00011-4
Importance of Metal Organic Frameworks - Nanografi Nano Technology. (n.d.). Retrieved July 9, 2024, from https://nanografi.com/blog/importance-of-metal-organic-frameworks/
Polymeric Coating - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics. (n.d.). Retrieved July 9, 2024, from https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/polymeric-coating
The Role of Nanotechnology in Aerospace - Nanografi Nano Technology. (n.d.). Retrieved July 9, 2024, from https://nanografi.com/blog/the-role-of-nanotechnology-in-aerospace/
The Use of Graphene-Based Materials in Anti-Corrosion Coatings - Nanografi Nano Technology. (n.d.). Retrieved July 9, 2024, from https://nanografi.com/blog/the-use-of-graphenebased-materials-in-anticorrosion-coatings/
Yadav, L., Sihmar, A., Kumar, S. et al. Review of nano-based smart coatings for corrosion mitigation: mechanisms, performance, and future prospects. Environ Sci Pollut Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33234-9
Yue, H., Wang, Z., & Zhen, Y. (2022). Recent Advances of Self-Healing Electronic Materials Applied in Organic Field-Effect Transistors. ACS Omega, 7(22), 18197–18205. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSOMEGA.2C00580
Recent Posts
-
Key Performance Metrics in Nanomaterials: How Performance Is Actually Evaluated
Introduction When nanomaterials are discussed, performance is often reduced isolated peak performanc …29th Jan 2026 -
Why Not All Graphene Is the Same: Structural Differences That Define Performance
Introduction Graphene is one of the most widely discussed materials in advanced technology, yet its …23rd Jan 2026 -
What Are Advanced Materials and Why They Matter for High-Tech Industries
Introduction Advanced materials are no longer peripheral inputs in technology development; they have …9th Jan 2026






