Titanium Aluminum Carbide (Ti3AlC2) MAX Phase Micron Powder, Purity: 99%, Size: 200 mesh, Industrial Grade
- SKU:
- NG10MPW1624
- Shipping:
- Calculated at Checkout
Description
25 grams: 93€
100 grams: 285€
500 grams: 745€
1000 grams: 1085€
Contact us for tailored quotes on larger quantities & experience exceptional solutions from our experts.
Titanium Aluminum Carbide (Ti3AlC2) MAX Phase Micron Powder
Purity: 99%, Size: 200 mesh, Industrial Grade
MAX Phase Ti3AlC2 is a representative of a unique class of ternary layered compounds that bridge the gap between conventional ceramics and metals. This industrial-grade dark grey powder possesses a distinct multi-layered, laminated morphology that is clearly visible under Scanning Electron Microscopy. This atomic-scale sandwich structure grants the material an extraordinary combination of properties: it retains the high-temperature stability, stiffness, and oxidation resistance of a ceramic while exhibiting the excellent electrical conductivity, thermal shock resistance, and damage tolerance typically associated with metals. Due to its layered nature, Ti3AlC2 acts as a versatile precursor for the synthesis of 2D MXene Ti3C2Tx nanosheets, making it a critical foundation for next-generation material science research and large-scale industrial manufacturing.
Technical Properties
| Purity | 99% | ||
| Size | 200 mesh | ||
| Structure | Multi-layered | ||
| Appearance | Dark Grey Powder | ||
| Elemental Analysis (%) | Ti | Al | C |
| 48 | 20 | 31 |
SEM Images
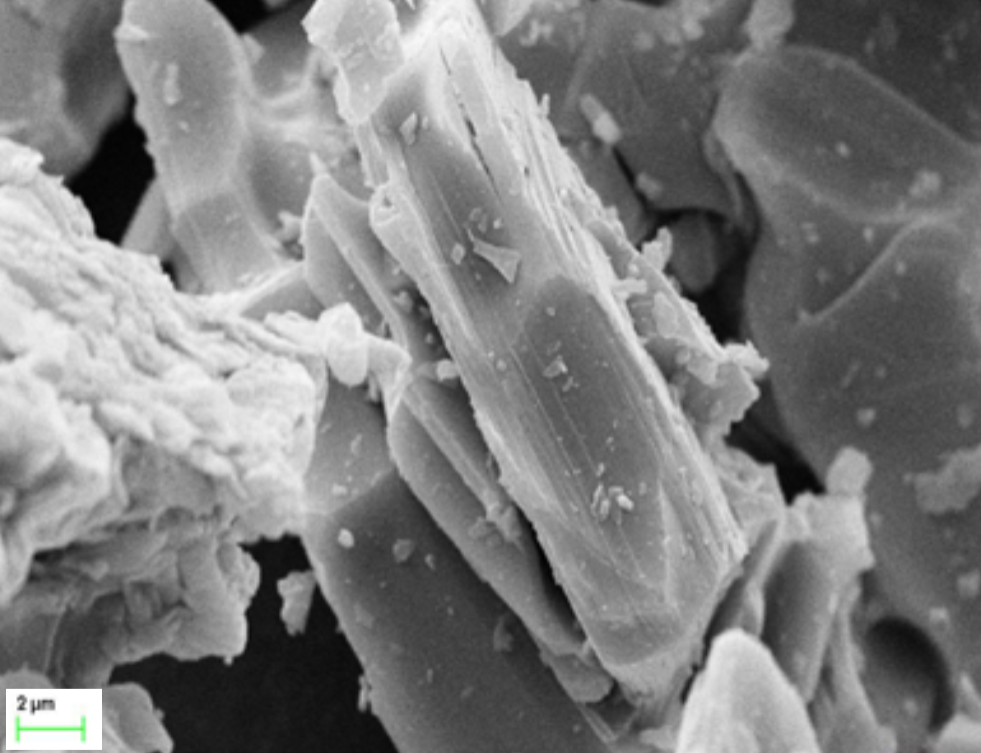

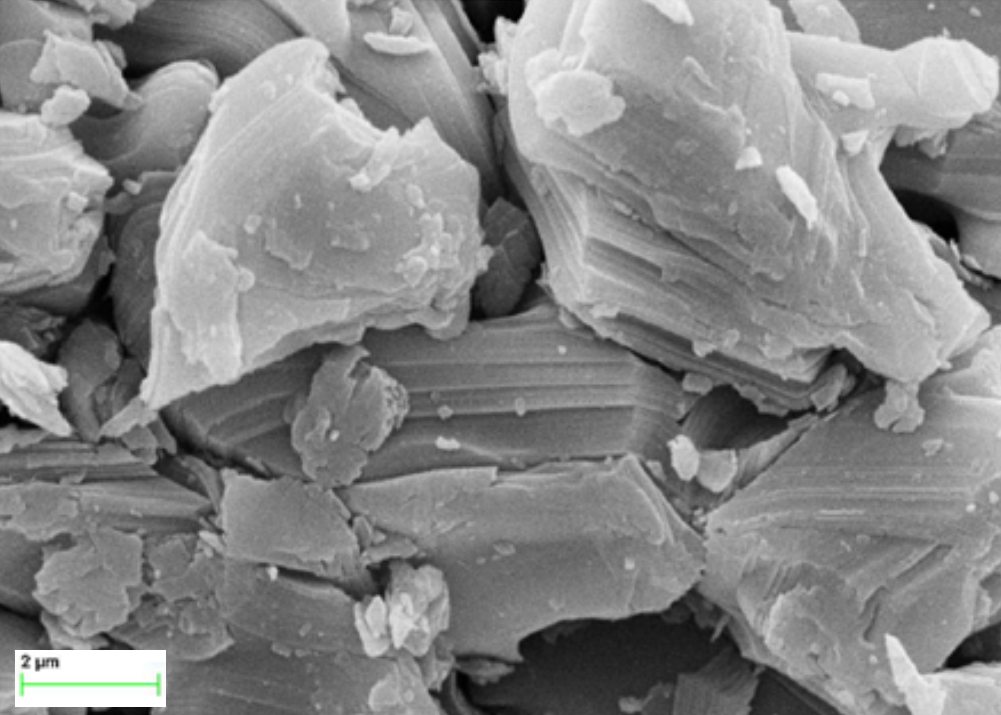
Applications
- MXene Precursor Synthesis: Primarily utilized as the essential raw material for etching into 2D MXenes, which are used in high-performance energy storage, sensors, and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding.
- High-Temperature Structural Components: Ideal for manufacturing aerospace and industrial parts that require durability under extreme thermal stress, combining metallic toughness with ceramic heat resistance.
- Conductive Ceramic Composites: Added to polymer or ceramic matrices to enhance electrical and thermal conductivity without sacrificing the mechanical integrity of the final composite.
- Nuclear and Energy Industry: Investigated for use in nuclear reactor components due to its resistance to radiation damage and high-temperature oxidation.
- Wear-Resistant Coatings: Applied in environments requiring low friction and high hardness, such as high-performance mechanical seals and engine components.
- Advanced Lubricants: The laminated, multi-layered structure allows the particles to slide against each other, serving as a high-efficiency solid lubricant in demanding industrial machinery.
- Electrode Materials: Used in the development of supercapacitors and battery electrodes where both chemical stability and high electron mobility are required.








